2021 AMC 10 B Fall
Complete problem set with solutions and individual problem pages
In square , points and lie on and , respectively. Segments and intersect at right angles at , with and . What is the area of the square?(2021 AMC Fall 10B, Question #15)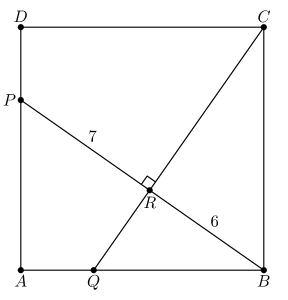
- A.
- B.
- C.
- D.
- E.
Solution 1:
Note that . Then, it follows that . Thus, . Define to be the length of side , then . Because is the altitude of the triangle, we can use the property that . Substituting the given lengths, we have Solving, gives and . We eliminate the possibilty of because . Thus, the side length of the square, by Pythagorean Theorem, is Thus, the area of the sqaure is . Thus, the answer is (D) 117
Solution 2:
As above, note that , which means that . In addition, note that is the altitude of a right triangle to its hypotenuse, so . Let the side length of the square be ; using similarity side ratios of to , we get Note that by the Pythagorean theorem, so we can use the expansion to produce two equations and two variables; We want , so we want to find . Subtracting the first equation from the second, we get Then
